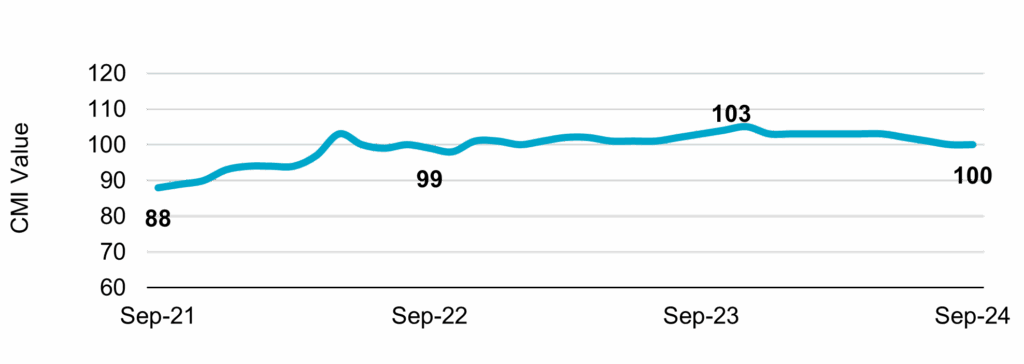
The Indian retail credit landscape witnessed a notable upswing in the July–September quarter of FY26, as GST Rate Rationalisation Boosts Retail Credit Market in Q2FY26, driven primarily by the revision of Goods and Services Tax (GST) implemented ahead of the festive season. According to TransUnion CIBIL’s Credit Market Report, the Credit Market Indicator (CMI) increased to 99 during Q2FY26, up from 98 in the preceding quarter. The GST revision appears to have played a catalytic role in stimulating borrowing appetite, especially in vehicle finance and consumer durables, which saw a pronounced surge in demand.
This shift in tax policy came at a strategic moment, coinciding with India’s most vibrant consumer spending period—festivals such as Ganesh Chaturthi, Navratri, and Diwali. These months traditionally witness heightened demand for personal loans, credit cards, electronics, and vehicles. As GST Rate Rationalisation Boosts Retail Credit Market in Q2FY26, the adjustment acted as a price reduction mechanism, encouraging more households to consider financed purchases. Consequently, the demand component of the CMI rose from 92 to 95, underscoring a renewed confidence among borrowers.
In this comprehensive analysis, we explore how GST Rate Rationalisation Boosts Retail Credit Market in Q2FY26, examining the interplay between GST policy changes, consumer sentiment, market behaviour, and lending performance. We also delve into how the credit ecosystem—banks, NBFCs, fintech lenders, and risk evaluators—responded to this shift, and what the future outlook could be for India’s credit landscape.
Understanding the Retail Credit Landscape in India
Retail credit has been a cornerstone of India’s financial growth story over the past decade. With rising digital penetration, expanding access to credit information, and the growing aspirations of a young population, the lending market has become more dynamic and inclusive. Traditionally, sectors such as housing, automobile finance, and personal loans have dominated portfolio growth. However, the retail lending space has also diversified to include consumer durable loans, BNPL (Buy Now Pay Later) schemes, and instant digital loans—trends that set the backdrop for how GST Rate Rationalisation Boosts Retail Credit Market in Q2FY26 by amplifying consumer borrowing potential.
The introduction of the Goods and Services Tax in 2017 marked a transformational moment for the Indian economy, unifying the indirect tax structure. Yet, periodic rationalisation continues to shape market behaviour significantly. The recent tweaks in GST rates were aimed at easing consumer costs during the festive months, making discretionary purchases more attractive. As a result, GST Rate Rationalisation Boosts Retail Credit Market in Q2FY26, with borrowing appetite increasing across consumer durables, vehicles, and short-term credit products—demonstrating a direct correlation between tax policy shifts and retail lending growth.
CMI Explained: A Snapshot of Credit Health

The Credit Market Indicator (CMI) serves as a holistic measure of retail credit health. It consolidates data from four pivotal pillars:
- Demand – consumer enquiry volumes and credit applications
- Supply – lender approvals and disbursements
- Consumer Behaviour – repayment discipline, credit usage, delinquencies
- Performance – portfolio quality and NPAs
The uptick from 98 to 99 may appear modest in absolute numbers, but within the structured CMI framework, such an increase suggests strong forward momentum. A rise in CMI typically reflects heightened borrowing activity, increased lender confidence, and healthy repayment patterns.
Importantly, the rise in demand CMI from 92 to 95 signals that the GST rationalisation had a direct and measureable impact on consumer appetite—especially for big-ticket and semi-durable items.
GST Rationalisation and Its Link to Consumer Credit Demand

When GST is reduced on specific goods—particularly automobiles, two-wheelers, appliances, and electronics—it lowers the effective market price. For millions of consumers, especially in middle-income households, this price drop can shift a purchase from aspirational to attainable.
Here’s how the GST cut worked as a growth catalyst:
1. Lower Upfront Costs → Higher Purchase Intent
For items such as:
- two-wheelers
- entry-level cars
- refrigerators
- washing machines
- smart TVs
even a marginal reduction in price makes EMI affordability more favourable. This encourages financing over full cash payments.
2. Easy Credit Availability Amplified the Effect
Banks and NBFCs actively rolled out:
- festival loan offers
- reduced interest rates
- zero-down payment schemes
- flexible tenure loans
- promotional tie-ups with manufacturers
These initiatives combined with GST effects triggered a rise in applications.
3. Strong Festive Sentiment as a Psychological Trigger
Culturally, Indians associate festivals with:
- home upgrades
- vehicle purchases
- gifting
- major expenses
A tax benefit during this period aligns perfectly with higher consumption sentiment.
Sector-Wise Breakdown of the Surge

1. Vehicle Finance
The two-wheeler and entry-level car segments were the biggest beneficiaries.
Reasons include:
- rising urban and semi-urban mobility needs
- increasing fuel-efficient and EV options
- aspirational ownership
- improved affordability due to GST cuts
Two-wheeler sales, often financed via NBFCs and micro-lenders, saw noticeable uplift. Auto loans followed suit.
2. Consumer Durable Loans
Products witnessing higher demand included:
- televisions
- refrigerators
- air conditioners
- mobile phones
- laptops
- kitchen appliances
With GST rationalisation shaving price points and EMI options reducing financial burden, consumers shifted preference toward mid-to-premium products.
3. Digital Lending: BNPL & Personal Loans
Fintech-powered models also grew as consumers sought:
- instant approvals
- low documentation
- quick disbursals
This reflects a maturing ecosystem where convenience complements affordability.
Impact on Lenders: Supply and Portfolio Performance

While demand surged, supply did not lag. Lenders increased disbursals thanks to:
- improved credit scoring models
- greater visibility via CIBIL reports
- strong borrower sentiment
Banks adopted cautious optimism, whereas NBFCs leveraged targeted retail campaigns.
Portfolio performance, measured under CMI, remained stable, indicating:
- controlled delinquencies
- steady repayments
- responsible borrowing
The absence of significant NPA shocks points to resilient market fundamentals.
Consumer Behaviour: The Responsible Borrower Trend
The rise in demand did not translate into reckless borrowing. Credit reports show:
- consumers continued timely repayments
- credit utilisation ratios remained within moderate bands
- credit card behaviour remained stable
Rather than impulse borrowing, this appears to be a rational response to favourable prices.
Economic Implications of GST-Driven Credit Growth

Policy changes influence economic cycles. The GST rationalisation contributed to:
Higher Consumption Expenditure
Particularly in:
- FMCG
- auto
- electronics
Boost to Manufacturing and Retail Sectors
Production cycles responded to increased demand, uplifting supply chains.
Expansion of Credit Penetration
More first-time borrowers entered the market, especially in tier-2 and tier-3 cities.
Improved Lending Confidence
With stable repayment behaviour, lenders continued to expand offerings.
Risks and Challenges Ahead

While the credit market is buoyant, potential concerns remain:
- rate hikes could affect borrowing cost
- inflationary pressures may slow demand
- macroeconomic uncertainty could impact consumption
- over-dependence on festive boosts may create seasonal volatility
Prudence must balance growth.
The Road Ahead: Outlook for FY26 and Beyond
Given current indicators:
- Retail credit demand is expected to remain robust
- Vehicle finance may continue outperforming due to EV push
- Consumer durables could sustain momentum if prices stabilize
- Digital lending will expand footprint
Policy interventions—if aligned with consumption trends—may support long-term credit market expansion.
The GST rationalisation is a textbook case of how tax policy, when timed and structured strategically, can influence consumer confidence and borrowing patterns.
For more details on GST rate changes, visit GST Council Official Website.
Read the full RRB IPO report on SkinnyZine.